

Heat is absorbed on one side of the pipe, by evaporation of the refrigerant, and released at the other side, by condensation of the refrigerant. The heat pipe uses multiple sealed pipes mounted in a coil configuration with fins to increase heat transfer. Heat Pipe: Operating in both opposing air paths, using a confined refrigerant as a heat transfer medium.

This device, although not very efficient, allows heat recovery between remote and sometimes multiple supply and exhaust airstreams.
 Run around coil: Two air to liquid heat exchanger coils, in opposing airstreams, piped together with a circulating pump and using water or a brine as the heat transfer medium. Wheels are also available with a hydroscopic coating to provide latent heat transfer and also the drying or humidification of airstreams. When the air handling unit is in cooling mode, heat is released as air passes through the matrix in the exhaust airstream, during one half rotation, and absorbed during the second half rotation into the supply airstream. When the air handling unit is in heating mode, heat is absorbed as air passes through the matrix in the exhaust airstream, during one half rotation, and released during the second half rotation into the supply airstream in a continuous process. Thermal Wheel, or Rotary heat exchanger: A slowly rotating matrix of finely corrugated metal, operating in both opposing airstreams. The plates are typically spaced at 4 to 6mm apart. Heat is transferred between airstreams from one side of the plate to the other. Recuperator, or Plate Heat exchanger: A sandwich of plastic or metal plates with interlaced air paths. This type of humidifier can quickly clog if the primary air filtration is not maintained in good order.Ī heat recovery device heat exchanger may be fitted to the air handler between supply and extract airstreams for energy savings and increasing capacity. As the air passes through the medium it entrains the water in fine droplets. Wetted medium: A fine fibrous medium in the airstream is kept moist with fresh water from a header pipe with a series of small outlets. Ultrasonic: A tray of fresh water in the airstream is excited by an ultrasonic device forming a fog or water mist. Spray mist: water is diffused either by a nozzle or other mechanical means into fine droplets and carried by the air. Vaporizer: steam or vapor from a boiler is blown directly into the air stream. The rate of evaporation can be increased by spraying the water onto baffles in the air stream. Evaporative: dry air blown over a reservoir will evaporate some of the water.
Run around coil: Two air to liquid heat exchanger coils, in opposing airstreams, piped together with a circulating pump and using water or a brine as the heat transfer medium. Wheels are also available with a hydroscopic coating to provide latent heat transfer and also the drying or humidification of airstreams. When the air handling unit is in cooling mode, heat is released as air passes through the matrix in the exhaust airstream, during one half rotation, and absorbed during the second half rotation into the supply airstream. When the air handling unit is in heating mode, heat is absorbed as air passes through the matrix in the exhaust airstream, during one half rotation, and released during the second half rotation into the supply airstream in a continuous process. Thermal Wheel, or Rotary heat exchanger: A slowly rotating matrix of finely corrugated metal, operating in both opposing airstreams. The plates are typically spaced at 4 to 6mm apart. Heat is transferred between airstreams from one side of the plate to the other. Recuperator, or Plate Heat exchanger: A sandwich of plastic or metal plates with interlaced air paths. This type of humidifier can quickly clog if the primary air filtration is not maintained in good order.Ī heat recovery device heat exchanger may be fitted to the air handler between supply and extract airstreams for energy savings and increasing capacity. As the air passes through the medium it entrains the water in fine droplets. Wetted medium: A fine fibrous medium in the airstream is kept moist with fresh water from a header pipe with a series of small outlets. Ultrasonic: A tray of fresh water in the airstream is excited by an ultrasonic device forming a fog or water mist. Spray mist: water is diffused either by a nozzle or other mechanical means into fine droplets and carried by the air. Vaporizer: steam or vapor from a boiler is blown directly into the air stream. The rate of evaporation can be increased by spraying the water onto baffles in the air stream. Evaporative: dry air blown over a reservoir will evaporate some of the water. 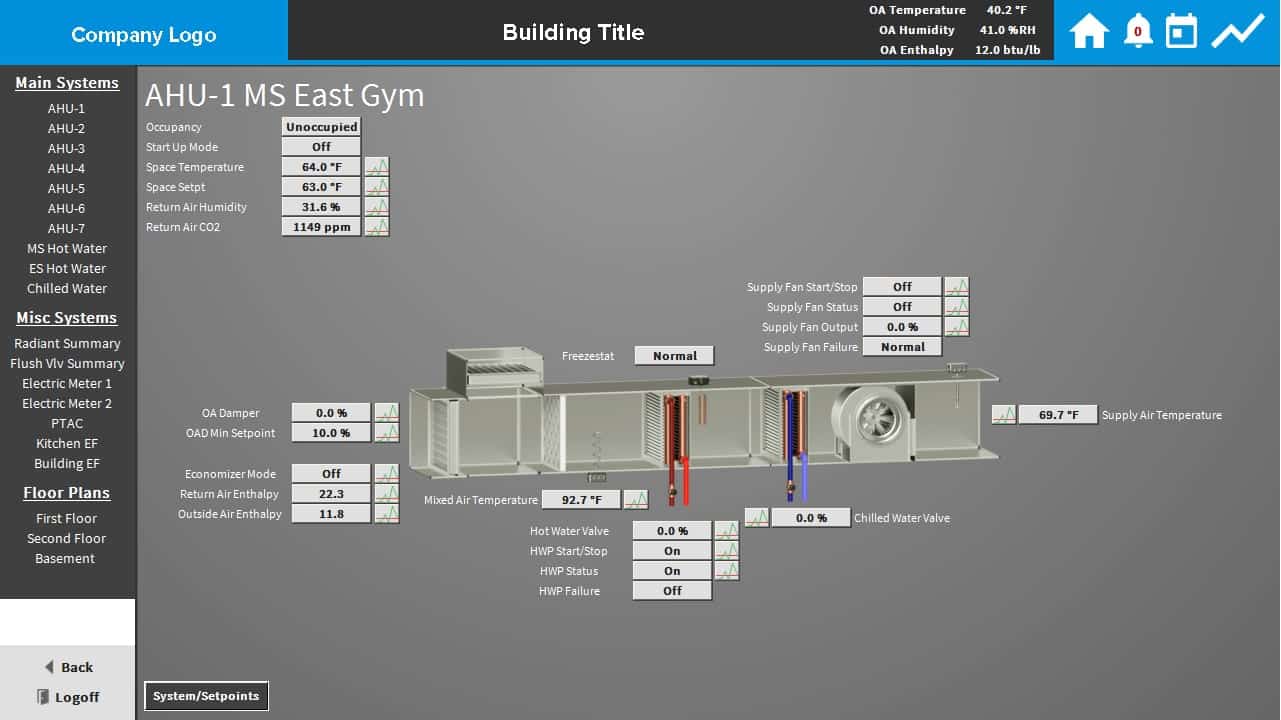
Various types of humidification may be used: Humidification is often necessary in colder climates where continuous heating will make the air drier, resulting in uncomfortable air quality and increased static electricity.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
